Bluestacks (#1 Android Emulator For PC) Blusestacks is one of the most common android. Download and install Genymotion Desktop for Windows, Mac or Linux and enjoy the latest Android versions on your machine. There are many ways to get Android running on a PC, including virtual device emulators, bootable USB versions, and even full standalone applications like BlueStacks. Each has its advantages. An Android Virtual Device (AVD) is a device configuration that runs on the Android Emulator. It provides virtual device-specific Android Environment in which we can install & test our Android Application. AVD Manager is a part of SDK Manager to create and manage the virtual devices created. To open AVD manager, go to Tools → Android → AVD. Your Android device needs to be on and connected to the same Wi-Fi network in order for this to work. The Your Phone app is connecting and mirroring apps to your PC from your Android phone. Can I access Android apps without linking my device? No, you need to connect your Android device to your PC via the Your Phone app in order to use this.
Google is committed to advancing racial equity for Black communities. See how.
You can use Android Emulator to create emulations of Android devicesthat run your own custom Android system images. You can also share your customAndroid system images so that other people can run emulations of them. Inaddition, you can add multi-display support to Android Emulatoremulations.
Android Emulator architecture
Android Emulator allows you to run emulations of Android devices on Windows,macOS or Linux machines. The Android Emulator runs the Android operating systemin a virtual machine called an Android Virtual Device (AVD). The AVD containsthe full Android softwarestack, and it runs as if itwere on a physical device. Figure 1 is a diagram of the Android Emulator'shigh-level architecture. For more information about the emulator, seeRun apps on the Android Emulator.
Figure 1. Android Emulator architecture
Building AVD images
Each AVD includes an Android system image, which runs inthat AVD. The AVD Manager includes some system images. And you can build customAVD system images from your source code and create device emulations to run them.
Note: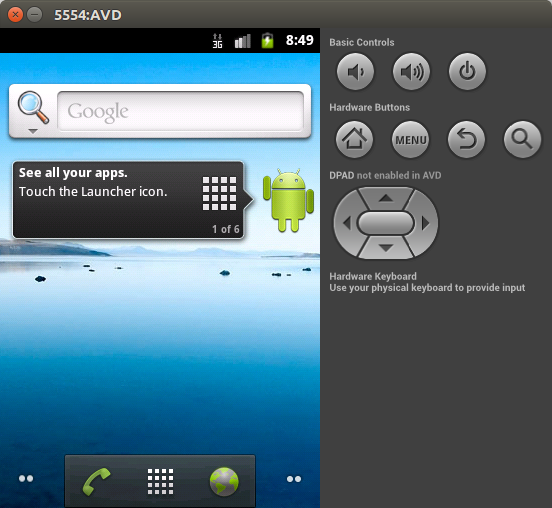 You need toestablish a build environmentbefore building AVD system images.
You need toestablish a build environmentbefore building AVD system images.To build and run an AVD system image:
Download the Android source:
If you want to build other Android versions, you can find theirbranch names inthe public Android repository.They map toAndroid Codenames, Tags, and Build Numbers.
Build an AVD system image. This is the same process as building anAndroid device systemimage. For example, to build a x86 32-bit AVD:
If you prefer to build an x86 64-bit AVD, run
lunchfor the 64-bit target:Run the AVD system image in the Android Emulator:
See theCommand-line startup optionsfor more details about running the emulator. Figure 2 shows an example of the Android Emulator running an AVD.
Figure 2. Android Emulator running an AVD
Sharing AVD system images for others to use with Android Studio
Follow these instructions to share your AVD system images with others. They canuse your AVD system images with AndroidStudio to develop and test apps.
Make additional
sdkandsdk_repopackages:This creates two files under
aosp-master/out/host/linux-x86/sdk/sdk_phone_x86:sdk-repo-linux-system-images-eng.[username].ziprepo-sys-img.xml
Host the file
sdk-repo-linux-system-images-eng.[username].zipsomewhere accessible to your users, and get its URL to use as the AVDSystem Image URL.Edit
repo-sys-img.xmlaccordingly:- Update
<sdk:url>to your AVD System Image URL. - Seesdk-sys-img-03.xsdto learn about other updates to the file.
- Update
Host
repo-sys-img.xmlsomewhere accessible to your users, and get itsURL to use as the Custom Update Site URL.
To use a custom AVD image, do the following in the SDK Manager:
Add the Custom Update Site URL as an SDK Update Site.
This adds your custom AVD system image to the System Images page.
Create an AVDby downloading and selecting the custom AVD system image.
Adding Multi-Display support
Virtual Android Phone On Pc
Android 10enhances Multi-Display (MD)to better support more use cases, such as auto and desktop mode. AndroidEmulator also supports multi-display emulation. So you can create a specificmulti-display environment without setting up the real hardware.
Android Virtual Device Manager
You can add multi-display support to an AVD by making the following changes, orby cherry picking fromthese CLs.
Add multi-display provider to the build by adding these lines to file
build/target/product/sdk_phone_x86.mk:Enable the Multi-Display feature flag by adding this line to file
device/generic/goldfish/data/etc/advancedFeatures.ini:
Android Studio Virtual Device
You can find the latest emulator features and release information fromthe following sources: